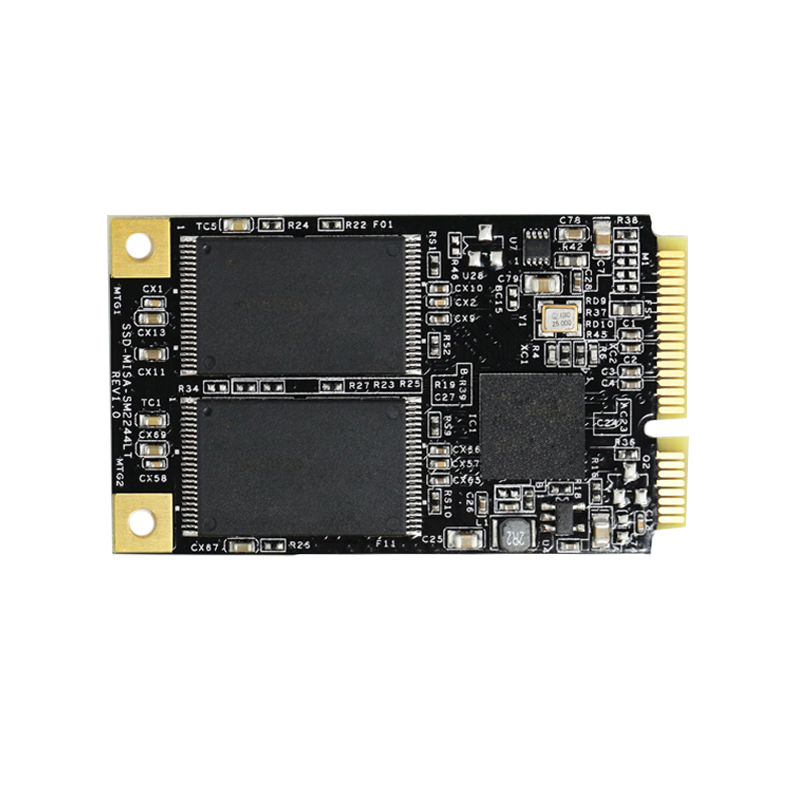
SATA (Serial Advanced Technology Attachment) is a computer bus interface that connects host bus adapters directly to mass storage devices like optical drives, solid-state drives, and hard disk drives. SATA first came into use in 2001 as a replacement for the earlier parallel ATA interface used in IBM compatible computers.
SATA was developed by a group of industry leaders and is based on the Serial ATA International Organization specifications. The standard supports data rates of up to 1.5 Gbit/s. SATA is the dominant storage interface for desktop and laptop computers.
The term “SATA” is often used interchangeably with the IDE interface that was the primary storage interface for most eras of Integrated Drive Electronics (IDE). However, IDE uses jumpers to speed up the transfer rate between a host and a storage device while SATA only utilizes a single cable. This means that IDE devices are much slower than their SATA counterparts, and that SATA drives have better endurance.
PATA drives deliver data bits simultaneously on a ribbon cable that's 40-pin wide. The SATA standard defines a SATA cable with two pairs of differential wires, three ground pins and a separate power connector.
These cables are less bulky than the ribbon cable used for PATA, allowing them to fit inside more compact systems and thinner notebooks. In addition, SATA's lower signal voltage of 250 millivolts compared to PATA's 5 volts reduces the risk of crosstalk and electromagnetic interference with other electrical circuits within the PC.
Another advantage of SATA is that it eliminates resource contention by dividing the connection into an independent computer host bus. This feature helps prevent data loss and improves performance over time.
Some SATA drives also have additional features such as device transmit emphasis and defined ordered NCQ commands, which can be useful in reducing latency. This revision of the SATA interface also added native command queueing, which is a type of processing optimization that allows SATA drives to optimize their data processing arrangement for optimal performance.
SATA drives are generally cheaper than those using the IDE interface. In fact, SATA is often the most affordable option for desktop and laptop computers.
Despite the cost advantage, SATA drives are still relatively slow compared to SSDs. This is because of the limitations of the SATA interface, which was originally designed for mechanical drives.
The SATA interface was later modified to support nonmechanical SSDs based on flash storage. This enables computers to transfer data to SSDs at much faster speeds than they could with SATA or SAS.
SATA devices can be found in desktop and laptop computers, as well as servers. The size of SATA drives depends on their intended use, with the most popular being 3.5-inch and 2.5-inch hard disks.

 EN
EN CN
CN ES
ES RU
RU